There are many decisions that factor into choosing what college you’ll attend. Among other important aspects, a big one is whether the school’s academic calendar is on a semester or quarter system.
The major differences between these two academic calendars is that in a semester system, students attend classes for two 15-week semesters per year; while in a quarter system, students attend classes for four 10-week quarters.
There are many other aspects that differentiate these two systems. Read on to learn more about semester vs. quarter systems and which one may be better for you!
What Is a Semester System?

A semester system divides the academic year into two 15-week sessions in the fall and spring, typically starting in August and concluding in May, with an optional “summer semester.” This is the most traditional way to structure an academic calendar — over 90% of colleges in the U.S. operate on a semester system.
How Long is a Semester?
Typically, a semester system is around 15 weeks long, though the exact length varies based on the specific school and holiday schedule. The fall semester typically starts in August and ends in December; the spring semester starts in January and ends in May.
Each semester is roughly divided into two sections with a break in the middle, traditionally a week-long fall and spring break. In general, schools on the semester system are on the following timetable:
- Fall semester: End of August through mid-December
- Spring semester: Mid-January through early May
- Summer semester (optional): June and July
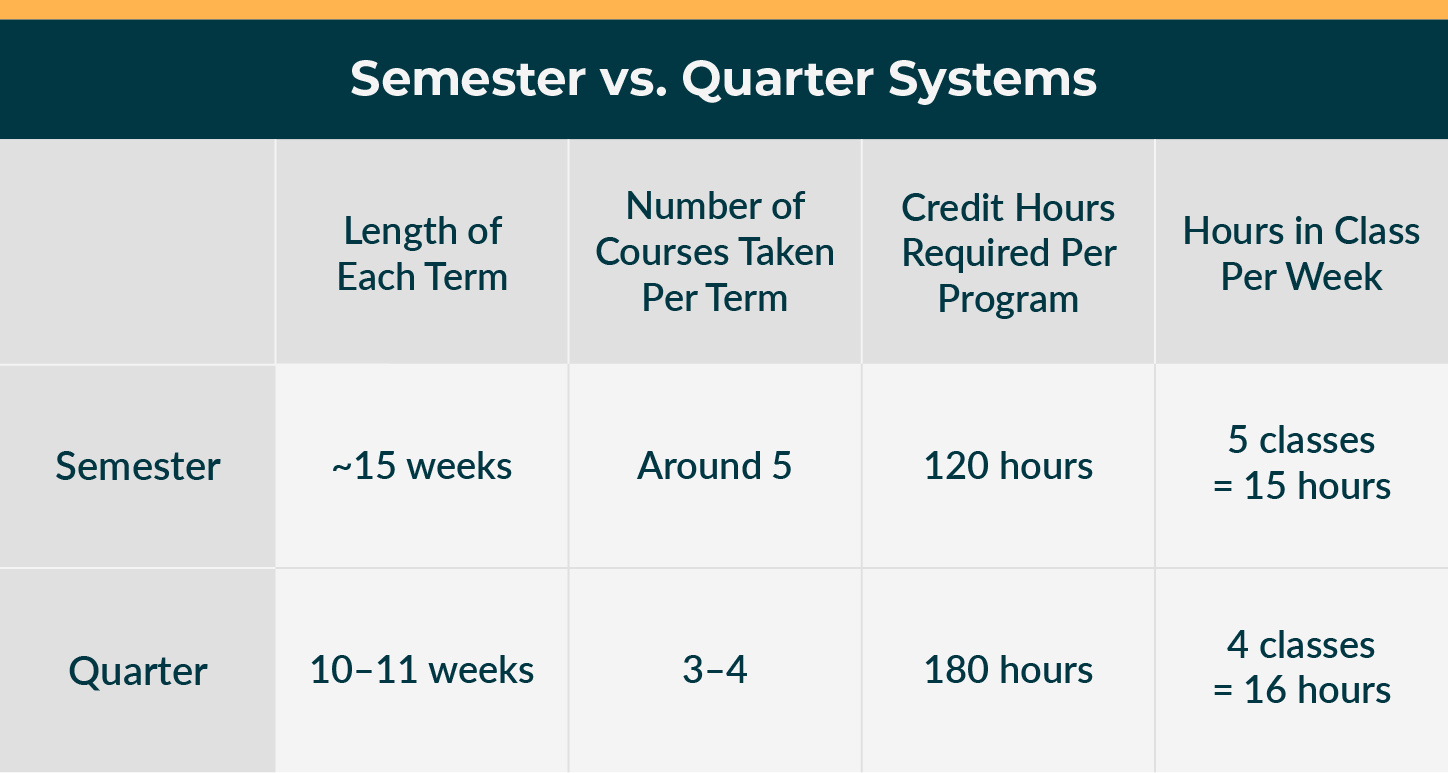
In general, a student will take roughly 15 credits per semester, for a total of 30 credits per academic year. Using these numbers, a student attending a school on the semester system will graduate having taken around 120 credit hours.
What Is a Quarter System?

In a quarter system, students attend classes for four 10- to 11-week quarters, divided into winter, spring, summer and fall.
How Long Is a Quarter in College?
Though exact schedules will vary from school to school, an average quarter is around 10 to 11 weeks long. Students will take around three to four classes per quarter, with each quarter coinciding with the seasons.
Much like the semester system, students are given a break at the end of each quarter before transitioning to the next one. The breaks between fall and winter quarter and spring and fall quarter are generally the longest, similar to a traditional winter and summer break.
On average, the quarter system is broken up in the following way:
- Fall quarter: mid-September through early December
- Winter quarter: early January through end of March
- Spring quarter: mid-April through early June
- Summer quarter: mid-June through end of August
In general, a student will take around 15 credit hours per quarter, taking classes three out of the four quarters for a total of 45 credit hours per year. Using these numbers, a student in a four-year program at a school on the quarter system graduates with approximately 180 credit hours.
Differences Between Semesters vs. Quarters

Though both the semester and quarter systems are used by institutions of higher education to design the academic calendar and award credit hours, the similarities end there. Neither system is inherently better than the other; but both have a number of differences.
To figure out which may be better for you in terms of workload, course credit and more, check out this table explaining what makes the semester and quarter systems so different.
Advantages of a Semester System
Since the semester system is so common in U.S. colleges and universities, there are many advantages for students when taking classes on a semester schedule.
1. More Time to Learn Information
One of the biggest advantages of a semester system is how long students have to absorb material. Having 15 weeks in one subject gives students a chance to not only learn the information for tests and assignments, but allows them to actually retain and absorb that information for future classes.
2. Time to Establish Student–Professor Relationships
Fifteen weeks, or roughly four months, with one professor gives students the opportunity to develop in-depth, positive relationships with professors. This helps students learn more from the professor given the longer time period. Plus, it gives students the opportunity to gain a professional reference when they’re applying for internships or jobs down the line.
3. Shorter Classes
With the exception of longer classes held once per week, many classes in the semester system are shorter than classes in quarter systems, often around 50 to 75 minutes. This can accommodate the busy schedules of college students and work well for their attention spans, which can be shorter during a particularly dry lecture class.
Disadvantages of a Semester System
Though there are several advantages of attending a university that runs on a semester system, there are disadvantages to consider as well.
1. Increased Stress
While 15 weeks is often more than enough time to thoroughly learn a course’s material, spending 15 weeks in anywhere from two to six classes that end at the same time can be stressful. This can lead to burnout, high levels of stress, poor performance and a negative impact on mental health.
2. Potential for Unnecessary Classes
On the semester system, students often have to take a certain number of classes per semester to remain full-time for scholarships and other forms of financial aid. This can lead to students taking “filler” classes each semester, or classes that don’t relate to their major just to fill up credit space.
3. Difficulty Improving GPA
Another disadvantage of the semester system is that classes generally carry more GPA weight each term. Due to this, a student who does poorly in a class one semester will have a hard time improving their cumulative GPA versus a student in a quarter system.
Advantages of a Quarter System
Though used less widely than the semester system, attending a college on the quarter system has some serious benefits of its own.
1. Smaller Work Loads
One big advantage of the quarter system is that students are taking less classes than students in a semester system. This smaller number of classes means a lighter workload per student, which can help reduce stress. This also means they have more time and brainpower to prepare for assignments, tests and projects in each of their classes.
2. More Class Flexibility
Having four opportunities per year to take a class gives students a lot of flexibility when it comes to building their schedule each semester. This allows students to experience more classes, make up or retake failed classes, take more elective courses and, overall, receive a well-rounded education.
In fact, a joint study by several universities showed that students on the quarter system take, on average, 18 more credits (or about six more classes) than their counterparts on the semester system.
3. Shorter Breaks
Having shorter breaks between quarters means students won’t experience the same “brain drain” as students on the semester system. This helps students with information recall and retention when they return to classes, which benefits their overall success in college.

Disadvantages of a Quarter System
While the quarter system certainly comes with some advantages, there are other disadvantages that may help inform your choice of whether or not to attend a school on this system.
1. Internship Difficulties
One of the biggest issues with the semester system being so widely adopted is that many internship schedules are set around fall and spring semesters, not quarters. This could make securing an internship (which many majors require) more difficult, or even require some students to choose between completing an internship or taking classes one quarter.
2. Study Abroad Interruptions
Studying abroad is something that many college students dream of. However, this is another opportunity that typically runs on the semester schedule; especially if students are taking classes at a partnering university in another country. Though it’s not impossible to study abroad while on the quarter system, this may require more research and legwork on the student’s end to find a school to do so.
3. Fast-Paced Classes
Though students are in fewer classes per quarter than their semester system counterparts, 10 to 11 weeks is still a very fast pace to learn an entire course’s worth of information. Especially when factoring in midterm assignments and final exams, some classes require students to learn the information in as little as eight weeks.
Semester Hours vs. Quarter Hours
If you’re a transfer student wondering how your quarter hours will transfer to a school on the semester system (or vice versa), wonder no more. Here’s a general breakdown of how semester hours are calculated versus quarter hours, and what that means for transfer students.
Generally, three quarters are equal to two semesters, or a 3/2 ratio. This is also expressed as 1.5 = 1.
Converting Quarter Hours to Semester Hours
To convert quarter credits to semester credits, divide quarter credits by 1.5, or: Quarter hours ÷ 1.5 = semester hours.
- 12 quarter hours ÷ 1.5 = 8 semester hours
- 9 quarter hours ÷ 1.5 = 6 quarter hours
- 3 quarter hours ÷ 1.5 = 2 semester hours
Converting Semester Hours to Quarter Hours
To convert semester hours to quarter hours, multiply semester credits by 1.5, or: Semester hours x 1.5 = quarter hours.
- 12 semester hours x 1.5 = 18 quarter hours
- 9 semester hours x 1.5 = 13.5 quarter hours
- 3 quarter hours x 1.5 = 4.5 quarter hours
What Is a Trimester?

The trimester system is another way of structuring a college’s academic calendar, though it’s less popular than either the quarter or semester systems. The trimester system functions very similarly to the quarter system, but divides the academic year into three sessions rather than four, with trimesters in the spring, fall and winter. Students take three to four classes per trimester.
How Long Is a Trimester?
The trimester system divides the year up into three 11 to 12 week sessions: one in the winter, one in the spring and one in the fall. This is structured similar to the quarter system, except the trimester system gives all students and faculty the summer off. Like the quarter system, students generally take around three to four classes per trimester.
To give you an idea of how the trimester system differs from the quarter and semester systems, here’s a general overview of what a trimester looks like.
- Fall trimester: Mid-September through early December
- Winter trimester: Early January through mid-March
- Spring trimester: Early April through mid-June
Choosing between schools on the quarter or semester system can be tough, as they both have unique advantages and opportunities. However, it’s important to choose what’s best for your learning style, work ethic and preferences. We’ll be here every step of the way, from everything you need to know about getting an English degree to when you need to know the best study apps.
Sources: Johnson & Wales University | Walla Walla Community College





