Universities vs colleges. Which is better college or university? You may be asking yourself this question. Prospective students, take note! This may help you choose the type of school you will attend.
The difference between college and university is an important one. With the interchangeable way the terms are used in conversation, the difference seems minor.
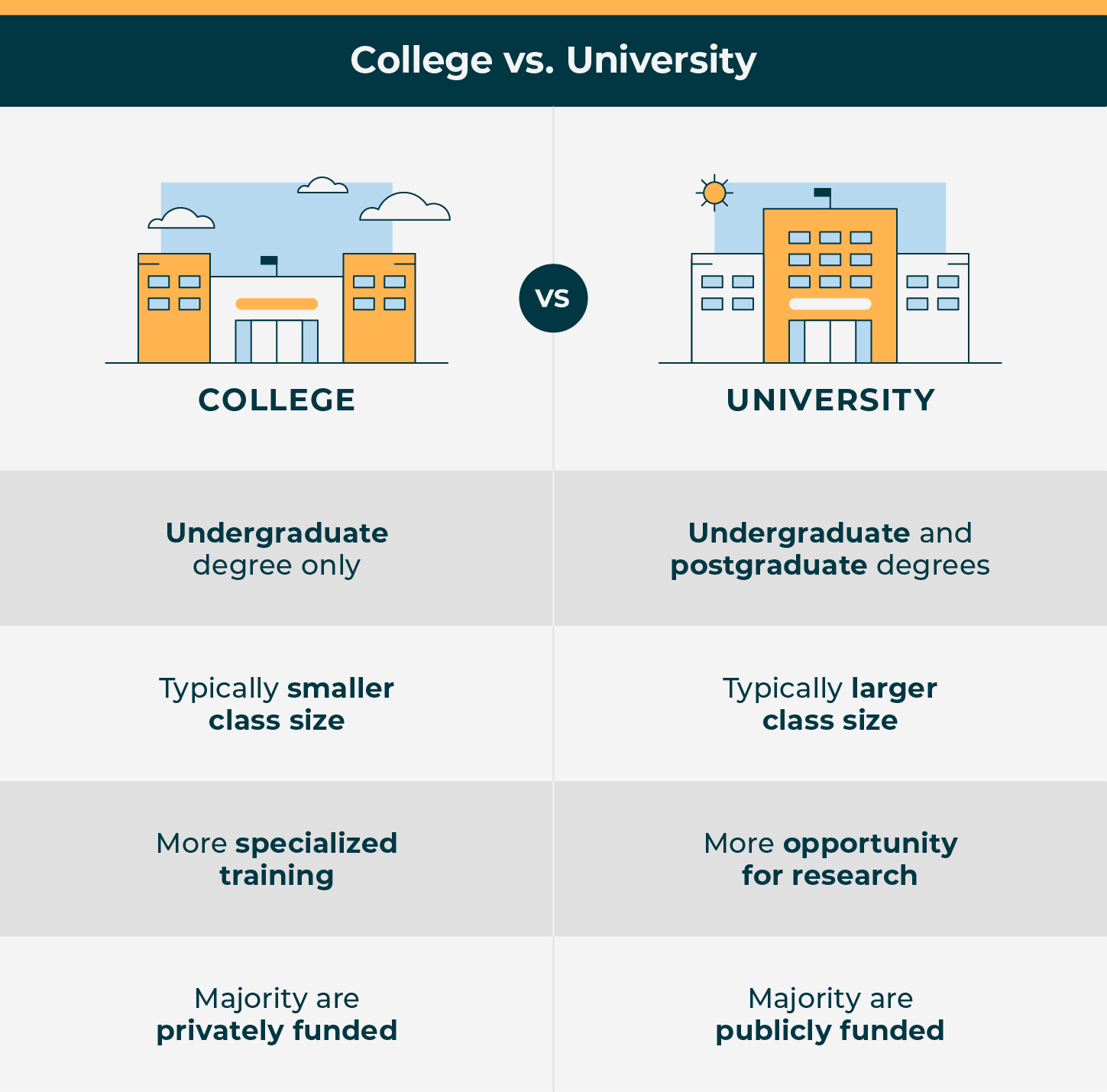
Generally, a college tends to be smaller. There is a more focused area of study. It doesn’t go beyond a four-year bachelor’s degree. A post-graduate program is a good indicator that the institution is a university. However, it’s important to know all the factors of the college and university difference.
Even if a student technically goes to a university, they’ll likely say they attend “college.” It’s how Americans speak about postsecondary education. This is because until you graduate from institutions of higher education, the difference isn’t as apparent. Colleges and universities:
- collect tuition fees
- offer various curricula
- prepare students for the professional workforce
- give out diplomas
- have accreditation
But once you get that diploma, the difference between attending a college and a university is a distinct one. Knowing the difference prior to graduation is crucial for your academic success. Different colleges and universities will offer features that appeal to you, but you can be set straight on the difference.
Colleges vs Universities
What Is a College?
A college in the USA is a smaller institution that offers undergraduate degrees. This includes two-year degrees. They are typically offered at two-year colleges, such as junior or community colleges. Or they offer bachelor’s degrees at four-year colleges. Some colleges also offer associate’s degrees. Some may be state-funded.
Colleges have other defining characteristics that separate them from universities. This is beyond offering undergraduate programs. Here are some key identifiers of the college and university difference:
- Degree program offerings. One main difference between college and university is in degree program offerings. Broadly speaking, colleges are post-secondary (meaning after high school) that focus mainly on undergraduate education.
- Colleges do not typically offer graduate degree programs. However, there are exceptions. They were founded as colleges and have grown to include graduate programs. This includes:
- Dartmouth College
- The College of William and Mary
- St. Joseph’s College
- Colleges typically offer smaller class sizes. This comes with more focused resources, such as advisors and one-on-one time with faculty. They’re also typically organized by subject-oriented departments. In a university setting, you may find larger classes and more resources going to research efforts.
- Colleges do not typically offer graduate degree programs. However, there are exceptions. They were founded as colleges and have grown to include graduate programs. This includes:
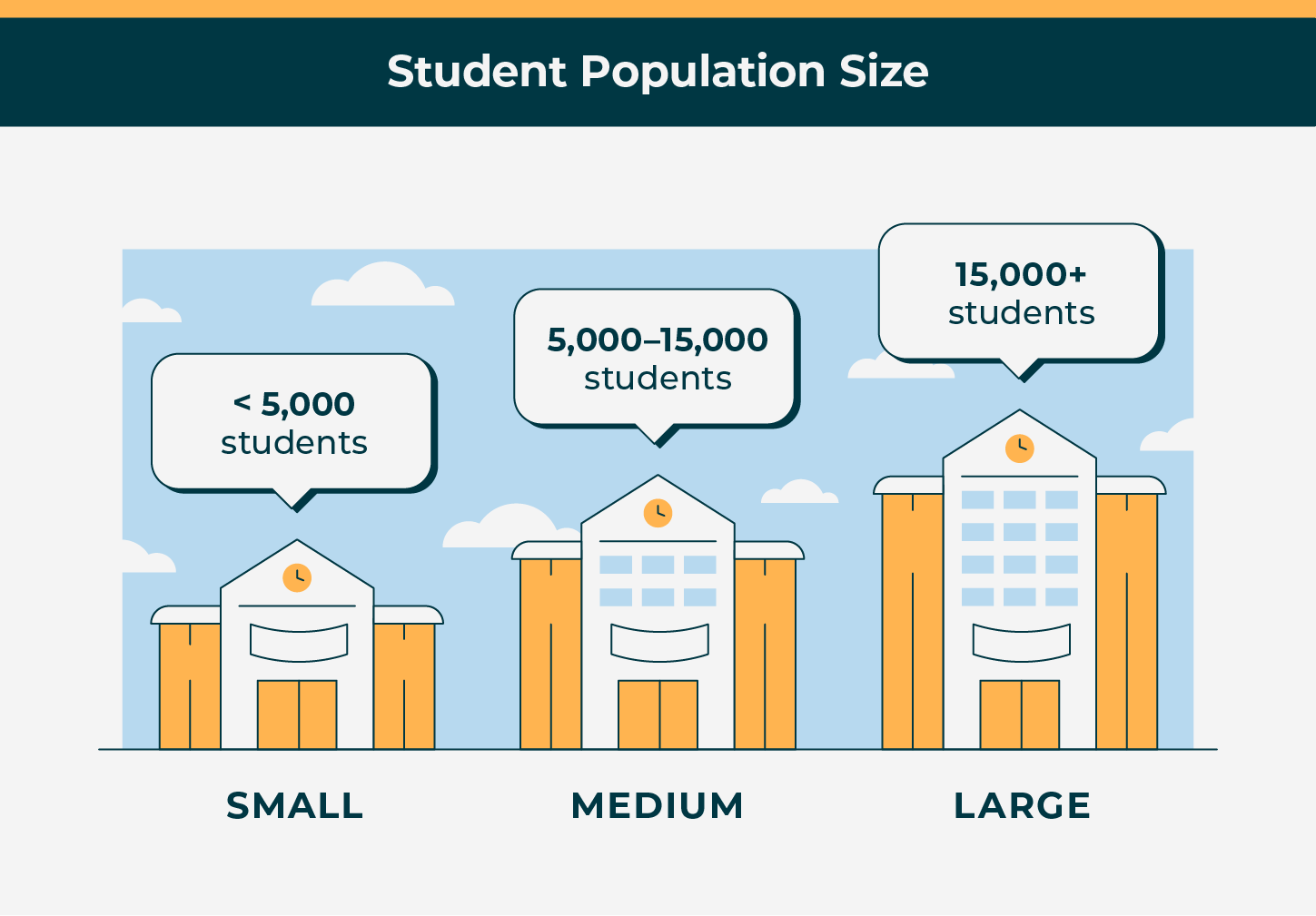
- Student population size. Colleges tend to be smaller than universities in terms of student body population size. Based on 2023 enrollment numbers, Western Governors University had the highest number of students enrolled with 150,116 students. By comparison, the largest college was Dallas College which had a total enrollment of 69,171.
- While the student body population at a college tends to be smaller, there is still some further classification to whether the college is “small,” “medium” or “large.”
- Based on a study by College Data, colleges considered “small” have fewer than 5,000 students. These small schools are likely to be private institutions. Colleges considered “medium” have between 5,000 and 15,000 students, and those considered “large” have more than 15,000 students. You can safely assume that these larger colleges are public state schools.
- Specialized schools. Colleges are more likely than universities to be specialized schools. This type of education focuses on a particular skill set or area of study.
- For example, the most common type of college is a liberal arts college. There are also:
- vocational schools-technical colleges
- arts colleges
- junior colleges
- For example, the most common type of college is a liberal arts college. There are also:
You can learn more about each below.
Types of Colleges
You now know what a college is, but let’s break that down further.
- Liberal arts. Liberal arts colleges gear their curricula to expose a broad base of knowledge. Completing a four-year program at a liberal arts college will award you with a bachelor’s degree. These institutions emphasize humanities subjects like:
- literature
- history
- languages
- mathematics
- life sciences
- Community and junior colleges. Education at a community college is more affordable and time-efficient. They offer two-year associate degrees that either prep you to transfer to a four-year college or graduate straight into a professional field. Your college experience can get off to a great start at a community college.
- Vocational-technical colleges. Vocational-technical colleges teach a specific skill set to use in a particular industry. If you are looking to get into the culinary arts, firefighting or medical-records technology, look into a vocational-technical college to master that specialty
- Arts colleges. Arts colleges place a particular emphasis on the arts. Supplemented with typical course work, these institutions practice intense training for areas such as:
- fine art
- fashion design
- theater
- music
- photography
We’ve explored what makes up a college. Now, let’s look at what defines a university to further learn the difference between a college vs university.
What Is a University?
While the word college is used more frequently, it doesn’t describe all higher education. It wasn’t the first of the two terms.
The term university was penned first in Middle English between 1250 CE and 1300 CE. It wasn’t until about 50 years later that the term college came along to describe more focused academic paths. In 1300 CE academic studies were numbered to math, arts and sciences. Middle English speakers understood a distinction needed to be made between a university vs college.
A university is often larger than a college and offers more majors and degrees. Like colleges, universities offer undergraduate degrees. They offer graduate degrees as well. Depending on where you’re studying, these can include master’s degrees and doctoral degrees.
Aside from offering more types of degrees, there are other factors that can help you identify whether an institution is a college or a university (without peeking at the name!).
- Most universities contain colleges within them. As mentioned above, universities can have colleges within them. Because of the various academic avenues you can pursue at a university, most are broken down into particular colleges that make up a university. For example, Penn State University has:
- the Smeal College of Business
- the Donald Bellisario College of Communications
- various other colleges
- Larger class size. Because of this wide offering, universities tend to enroll more students. Their resources are distributed between undergraduate students as well as graduate students and researchers.
A larger student population also means more intense extracurricular activities. Universities often have the top sports teams and more robust student organization options.
Types of Universities
Another misconception is that all universities are public. Although most colleges are typically privately funded and most universities are publicly funded, there are exceptions. Here are the terms to look out for:
- Private university. Although private schools tend to be colleges, there are a few private universities, like Ivy League schools. Private schools are financed by:
- alumni contributors
- tuition
- Public universities. A public university is mostly financed by a state or local government. Notably, public schools tend to be universities. They receive a larger influx of public money which can be used to set up more programs, research wings and a larger institution.
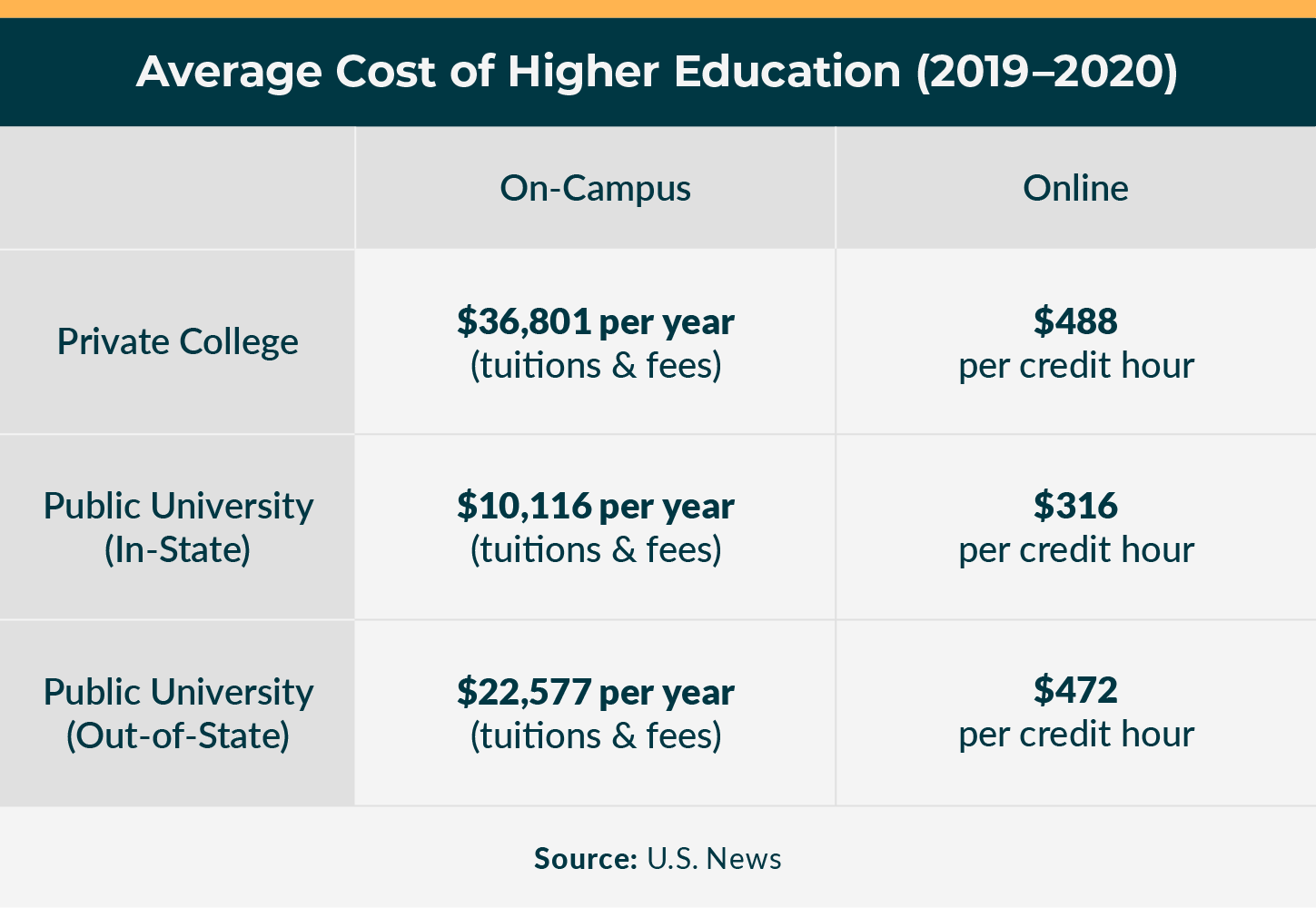
- The funding between public and private schools is important. This is not only because it is yet another differentiator between universities and colleges. More practically it means private schools are more expensive than public schools. The average cost of tuition and fees for a private college is $36,801, whereas the average cost of tuition and fees for a public university is $10,116 for in-state students and $22,577 for out-of-state students, based on U.S. News data.
- Research universities. Research universities place a heavy emphasis on exploration of a topic and analysis. These universities have four-year programs to receive a bachelor’s degree. They have tracks to carry out education through a doctorate degree. Undergraduate students can participate in research opportunities. Universities are geared towards graduate and doctoral students conducting intensive research.
In general, the main difference between a college and a university is the offering of a graduate degree. So, if you are looking to carry out your education beyond a four-year bachelor’s degree, then consider a university.
However, postgraduate education isn’t the only thing to consider in weighing this decision. Things like your area of interest, professional aspiration and budget largely impact your choice to either attend a college vs university.
Which Is Better: A College or a University?
When it comes to attending a college or a university, it isn’t so much which is better, but which one fits best for you. There are pros and cons to attending a college or a university. Here are the key considerations for university vs college:
- Area of study: Are you the kind of person who has already decided on an area of study? If yes, then you may want to consider a specialty college, such as an engineering school. If you already know what it is you want to specialize in, then do some research as to which university or college has the best program for that specialty.
- If you’re undecided, getting a liberal arts education will expose you to a general knowledge base. You’ll get a taste of:
- life sciences
- writing
- math
- philosophy
- For some additional help, here’s a breakdown of the average base starting salaries of the Class of 2020 graduates one year after graduation based on their area of study, according to Indeed.
- If you’re undecided, getting a liberal arts education will expose you to a general knowledge base. You’ll get a taste of:

- Career path: Do you know what you want to do after school? If you already have a career in mind and are ready to join the workforce, you may want to consider an associate degree program. Or you can consider a two-year community college. You can begin earning a paycheck sooner rather than later.
- Price: Ask yourself — do you really want to be riddled with student debt? Understand your financial situation. Keep in mind the cost of a public school vs private school. You can use loan financing to cover tuition and fees. You don’t want to get yourself into too deep of a hole. Paying back student loans can be a lifelong struggle if you consistently make decisions outside of your financial capacity. We recommend talking with:
- your parents
- guardians
- the financial aid offices at schools
College is expensive, but another option to save on cost is attending an online school. There are both online universities and online colleges. The difference between the two carries true online. Universities online provide postgraduate degrees whereas online colleges for the most part only offer undergraduate diplomas.
Online Higher Education
Things like student body size and price may deter you from applying to a college or university. You might want to consider attending an online higher education institution.
Online education is on the rise. According to Insider Higher Ed, the number of learners taking at least one online course grew from 31.1 percent in 2016 to 33.1 percent in 2017 and 34.7 percent in 2018.

One reason for this rise is the flexibility and advanced degree programs offered by online schools.
Additionally, online colleges and universities have lower tuition prices. They offer more adaptable schedules. If you’re attending school while working a full-time job, pursuing an online education might be the best fit for your schedule.
Another major advantage of online schools is the opportunity to get a degree without leaving your home and uprooting to campus.
Now that you know the difference between colleges vs. universities, you can confidently pursue whichever makes the most sense for you.
No matter what you decide, you will have:
- a solid course load
- a fair share of homework
- plenty of opportunities to learn tons of new things
Handling higher education can be difficult in any setting.
Check out our guide to help you gracefully move through school, no matter if you find yourself in:
- a two-year private college
- a master’s program at a university
- a continued education course through an online university
Keep it handy for those busy times when deadlines come up fast and work piles on!
Sources: College Data | U.S News | U.S News Data | Inside HigherEd | Big Future | Classes and Careers | College Raptor | Indeed
Find some best colleges and universities: